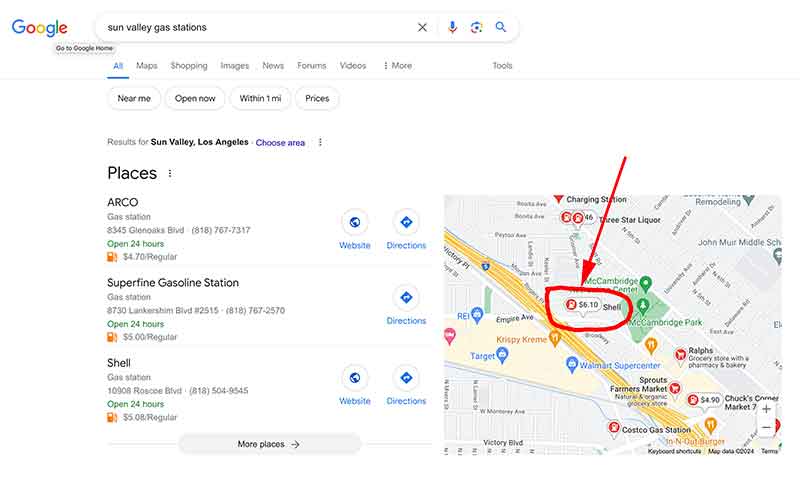
Jose Mier has checked Sun Valley, CA gas prices in the past but in the last week prices seem to have skyrocketed. Check out Gas Buddy for the latest info on these stations and prices.
California is known for many things: its beautiful coastline, diverse culture, and booming tech industry. However, it is also notorious for having some of the highest gasoline prices in the United States. Understanding why gas prices in California are so high involves examining a range of factors, from environmental regulations to market dynamics. This comprehensive analysis will explore the causes of high gas prices in California, their impacts on residents and businesses, and potential solutions for the future.
1. Causes of High Gas Prices in California
1.1. Stringent Environmental Regulations
California has some of the strictest environmental regulations in the country. The state mandates the use of a unique blend of gasoline known as CARB (California Air Resources Board) gasoline, designed to reduce air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. While these regulations help protect the environment and public health, they also increase production costs for refineries. The special formulation required for CARB gasoline is more expensive to produce than conventional gasoline used in other states.
1.2. Taxes and Fees
California imposes higher taxes on gasoline compared to most other states. As of mid-2024, the state excise tax on gasoline is 53.9 cents per gallon, the highest in the nation. Additionally, California drivers pay other fees, such as the cap-and-trade program costs and underground storage tank fees. Combined, these taxes and fees significantly increase the price at the pump for California consumers.
1.3. Limited Refining Capacity
California has a limited number of refineries capable of producing CARB-compliant gasoline. This limited refining capacity can lead to supply constraints, especially when refineries undergo maintenance or unexpected shutdowns. Any disruption in supply can cause a significant spike in gasoline prices due to the state’s reliance on a few refineries.
1.4. Geographic Isolation
California’s geographic isolation from other major refining hubs in the U.S. means that it is more difficult and costly to import gasoline. Unlike states in the Midwest or along the Gulf Coast, which can easily receive gasoline from neighboring states or countries, California must rely on shipping fuel from distant locations, adding to the overall cost.
1.5. High Demand
California is the most populous state in the U.S., with a high demand for gasoline due to its vast size, significant commuting distances, and reliance on automobiles. This high demand, coupled with the factors mentioned above, contributes to persistently high gasoline prices.
2. Impacts of High Gas Prices on California
2.1. Economic Impact
High gasoline prices have a ripple effect on the economy. When fuel costs rise, the cost of transporting goods increases, leading to higher prices for consumer products. This contributes to inflation, which can erode purchasing power and slow economic growth. Businesses, particularly those heavily reliant on transportation, such as trucking and delivery services, face increased operating costs, which can reduce profitability and lead to higher prices for consumers.
2.2. Impact on Households
For many California residents, high gasoline prices mean higher living costs. Commuters who drive long distances to work are particularly affected, as they must allocate a larger portion of their budget to fuel expenses. This can lead to reduced discretionary spending, affecting local businesses and the broader economy. Lower-income households are disproportionately impacted, as they spend a higher percentage of their income on transportation costs.
2.3. Environmental Impact
While high gasoline prices can have negative economic effects, they also have the potential to drive positive environmental outcomes. Higher fuel costs can incentivize consumers to adopt more fuel-efficient vehicles, use public transportation, or switch to alternative modes of transportation such as biking or walking. Over time, this can lead to reduced greenhouse gas emissions and improved air quality.
2.4. Social and Behavioral Impact
High gasoline prices can also lead to changes in social behavior. Carpooling, telecommuting, and other cost-saving measures become more attractive when fuel prices are high. Additionally, there may be increased interest in electric vehicles (EVs) and other sustainable transportation options, leading to a shift in consumer preferences and market trends.
3. Addressing High Gas Prices: Potential Solutions
3.1. Expanding Refining Capacity
One potential solution to high gasoline prices is to expand refining capacity within California. Increasing the number of refineries capable of producing CARB-compliant gasoline could help stabilize supply and reduce price volatility. However, this approach faces significant challenges, including environmental concerns, regulatory hurdles, and the high cost of building new refineries.
3.2. Investing in Renewable Energy
Investing in renewable energy sources and technologies can help reduce reliance on gasoline and lower transportation costs in the long term. California has been a leader in promoting renewable energy, and continued investment in solar, wind, and other clean energy sources can support the transition to a more sustainable transportation system. Incentives for electric vehicles and the development of charging infrastructure are also critical components of this strategy.
3.3. Enhancing Public Transportation
Improving public transportation infrastructure can provide an affordable and efficient alternative to driving, reducing demand for gasoline. Expanding and modernizing public transit systems, such as buses, trains, and light rail, can help ease traffic congestion, lower emissions, and provide residents with convenient travel options.
3.4. Encouraging Fuel Efficiency
Policies that encourage the adoption of fuel-efficient vehicles can help mitigate the impact of high gasoline prices. This includes offering incentives for hybrid and electric vehicles, implementing stricter fuel economy standards, and promoting the development of new technologies that improve fuel efficiency.
3.5. Addressing Regulatory and Taxation Issues
While environmental regulations and taxes are essential for promoting sustainability, finding a balance that minimizes economic impact is crucial. Policymakers could consider adjusting tax rates or providing temporary relief during periods of exceptionally high gasoline prices. Streamlining regulatory processes to facilitate the construction and expansion of refineries could also help increase supply and stabilize prices.
4. Future Outlook
The future of gasoline prices in California will likely be shaped by a combination of market dynamics, technological advancements, and policy decisions. As the state continues to pursue ambitious climate goals and promote sustainable transportation, the reliance on gasoline is expected to decrease over time. However, this transition will require significant investment and coordination across various sectors.
4.1. Transition to Electric Vehicles
The shift towards electric vehicles (EVs) is already underway in California, driven by state incentives, advancements in battery technology, and growing consumer awareness of environmental issues. As EV adoption increases, the demand for gasoline is expected to decline, potentially leading to lower prices. However, this transition will take time, and gasoline will remain an essential fuel for many years to come.
4.2. Technological Innovations
Technological innovations in fuel efficiency, alternative fuels, and transportation systems will play a critical role in shaping the future of gasoline prices. Continued research and development in these areas can lead to more cost-effective and sustainable solutions, reducing the overall demand for gasoline and mitigating price volatility.
4.3. Policy and Regulatory Developments
Policy and regulatory developments at the state and federal levels will significantly impact gasoline prices. California’s commitment to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting clean energy will drive policy decisions aimed at decreasing reliance on fossil fuels. Collaborative efforts between government, industry, and stakeholders will be essential in developing effective strategies to address high gasoline prices while ensuring economic stability and environmental sustainability.
Conclusion
High gasoline prices in California are the result of a complex interplay of factors, including stringent environmental regulations, high taxes, limited refining capacity, geographic isolation, and high demand. These prices have far-reaching impacts on the economy, households, the environment, and social behavior. Addressing high gasoline prices requires a multifaceted approach that includes expanding refining capacity, investing in renewable energy, enhancing public transportation, encouraging fuel efficiency, and balancing regulatory and taxation issues.
As California continues to lead the nation in environmental initiatives and the transition to sustainable transportation, the future outlook for gasoline prices will be shaped by technological advancements, policy developments, and market dynamics. While the journey towards reducing reliance on gasoline and achieving a more sustainable transportation system is complex and challenging, it holds the promise of a cleaner, more resilient, and economically stable future for all Californians.